Hash Functions – The Building Block of Integrity
Intent:
To explain how cryptographic hash functions ensure blockchain integrity, immutability, and trustless verification.
Introduction – Why Hash Functions Matter
At the core of blockchain’s tamper – proof design lies one powerful concept: the hash function.
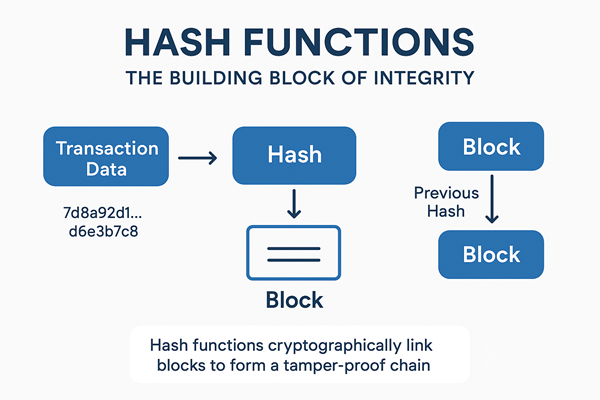
A hash function takes data of any size – a simple message, an entire block, or even a digital contract — and turns it into a unique, fixed-length string called a hash. This process ensures that any change, no matter how small, produces an entirely different result.
In short, hash functions serve as digital fingerprints for every piece of data on the blockchain. They don’t just protect information — they guarantee its integrity, making trust possible without intermediaries.
What Is a Hash Function?
A hash function is a mathematical algorithm that converts input data into a unique output — a short, alphanumeric string known as a hash value or digest.
For example:
Input: “Blockchain”
Output: “2c26b46b68ffc68ff99b453c1d30413413422f1640d775… (SHA-256)”
Even changing one letter — say, “blockchain” → “Blockchain” — completely alters the hash output.
This one-way process makes it impossible to reconstruct the original data from the hash, ensuring security and anonymity.
How Hash Functions Work in Blockchain
Each block in a blockchain uses hash functions in multiple critical ways:
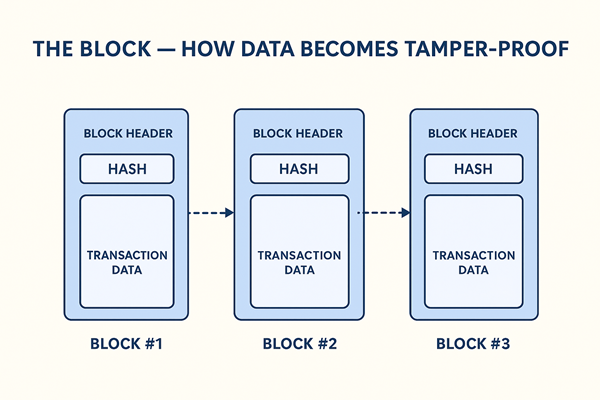
- Block Identification – Every block is assigned a unique hash that acts as its digital ID.
- Linking Blocks Together – Each block contains the previous block’s hash, creating a chain of trust.
- Tamper Detection – If any transaction is modified, its hash changes — immediately invalidating the block.
- Consensus Validation – Hashes play a key role in Proof-of-Work, ensuring miners perform verifiable computations.
This system ensures that data integrity is mathematically verifiable, not dependent on trust.
Why Hashes Are Irreversible
Hashing is a one-way function – it’s designed to be easy to compute but practically impossible to reverse.
Even with immense computing power, reconstructing the original input from its hash would take longer than the age of the universe.
That’s why blockchain data, once recorded and hashed, is permanent and tamper-proof.
Popular Hash Functions in Blockchain
| Algorithm | Used By | Output Size | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| SHA-256 | Bitcoin, many others | 256 bits | Block hashing, mining |
| Keccak-256 | Ethereum | 256 bits | Smart contract verification |
| Blake2b | Zcash, Filecoin | Variable | Speed and energy efficiency |
Each serves the same fundamental role — preserving data integrity and enabling consensus.
Real-World Analogy
Think of hashing like sealing a document with a unique wax stamp.
If someone changes even a single word in the document, the wax seal no longer matches — exposing tampering instantly.
That’s precisely how hash functions authenticate digital information on blockchains.
The Role of Hashing in Blockchain Integrity
Hash functions are the heartbeat of blockchain trust.
They:
- Ensure immutability of data.
- Allow tamper detection without human oversight.
- Enable efficient consensus mechanisms.
- Build confidence in decentralized systems.
Without hashing, blockchain would be just a regular distributed database — mutable, insecure, and unreliable.
Visualizing Hashing in Action
A simple conceptual flow:
[Transaction Data]
↓
Hash Function
↓
[Unique Hash Output]
Then:
Each new block → includes hash of previous block → forming a chain → if one block changes, all following hashes break → making alteration detectable.
Key Takeaway
Hash functions turn blockchain into a system of trust without trust.
They convert data integrity into mathematics — a concept that reshapes how we think about digital security, verification, and transparency.
Blockchain without hashing isn’t blockchain at all — it’s just a record.
Hashing gives it truth.